
Banking Trojan Adds Hidden VNC Full Remote Control for Attackers
A newly discovered Android banking trojan combines overlay attacks with a stealthy hidden VNC server to gain full remote control over compromised devices.

A newly discovered Android banking trojan combines overlay attacks with a stealthy hidden VNC server to gain full remote control over compromised devices.
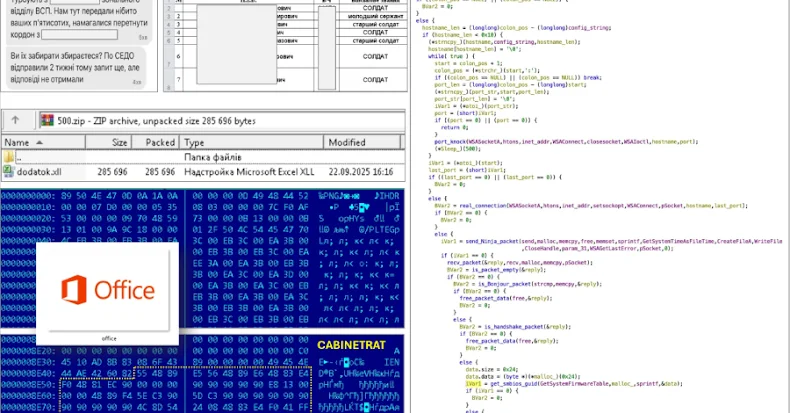
Ukraine’s CERT-UA has warned that CabinetRAT backdoor malware is being actively deployed in cyber espionage campaigns targeting government and critical networks.

Researchers have uncovered a new cybercriminal toolkit called MatrixPDF, designed to transform normal PDF files into weapons for phishing and malware delivery. This toolkit lowers the barrier for attackers. In fact, it provides ready made templates that let even inexperienced hackers craft PDF lures capable of bypassing security filters. As a result, phishing campaigns become…
A malicious MCP server can exfiltrate API keys and sensitive data from applications, exposing how trust in developer frameworks can be abused.

EvilAI operators are hiding malware in legitimate-looking AI tools that appear functional and signed, enabling reconnaissance, browser data exfiltration, and encrypted C2 communication across global targets.

Hackers posing as Medusa agents tried to lure BBC’s Joe Tidy into facilitating a cyberattack, offering him 15–25% of ransom payouts in exchange for his laptop’s access to the network.

Threat actors are increasingly poisoning AI tools and assistants embedding dangerous prompts or corrupting the data they rely on to turn defenses against organizations.

A sophisticated cyber campaign used DLL side‑loading to deliver a hybrid PlugX variant and the Bookworm backdoor to telecom and ASEAN networks, revealing renewed tactics by China‑linked threat actors.

A targeted malvertising campaign redirected users from Bing to a fake Teams download site, where a signed MSTeamsSetup.exe installed the Oyster backdoor — blocked just in time by Microsoft Defender ASR.

The new LAMEHUG malware uses AI models from Hugging Face to generate Windows commands dynamically. It spreads through phishing, disguises itself as AI apps, and steals system data, documents, and credentials while adapting to different environments.